Some important questions class 10th science Chapter 12 LIGHT -REFLECTION OF LIGHT
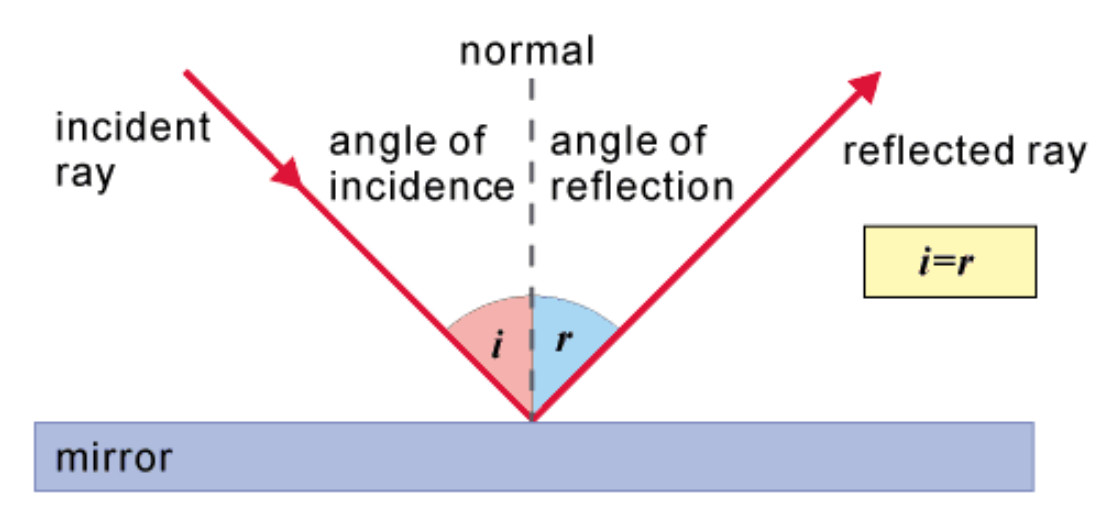
1. Define the term "reflection of light". State the laws of reflection and explain them with the help of a labeled diagram.
Answer: The reflection of light refers to the bouncing back of light rays from a surface when they strike it.
laws of reflection
:
i.
The incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal to the surface at
the point of incidence all lie in the same plane.
ii.
The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection, measured
from the normal to the surface.
2.
How is the angle of incidence related to the angle of reflection?
State the mathematical relationship.
Answer: The angle of incidence is related to the angle of reflection through the laws of reflection. According to these laws, the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Formula:
Angle of Incidence = Angle of Reflection.
3.
Give properties of the image formed by the plane mirror.
Answer: The properties of the image formed by a plane mirror are as follows:
i.
The image formed is virtual, meaning it cannot be obtained on a
screen.
ii.
The image formed is erect, which means it appears in the same
orientation as the object.
iii.
The image formed is of the same size as the object.
iv.
The image formed is laterally inverted, which means left and right are
interchanged in the image compared to the object.
4.
Explain the concept of lateral inversion in the context of a plane
mirror.
Answer: Lateral inversion means the reversal of the left-right Side of an object in its image formed by the mirror.
For example, if you raise your right hand in front of a plane mirror, the image in the mirror appears to raise its left hand. This reversal of sides is known as lateral inversion.
5.
Explain the formation of an image by a concave mirror when the object
is placed beyond the center of curvature.
Answer: When an object is placed beyond the center of curvature of a concave mirror, an inverted and real image is formed. The image is smaller in size than the object. The rays of light from the top of the object converge after reflection and meet at a point in front of the mirror, forming the image. This point of convergence is located between the focal point and the center of curvature.
6.
Define the term "focal length" of a concave mirror. How is it related
to the radius of curvature?
Answer: The focal length of a concave mirror is the distance between the focal point and the mirror's surface. It is denoted by 'f'. The focal length is related to the radius of curvature (R) of the mirror through the formula: f = R/2.
7.
What are the properties of the image formed by a concave mirror when
the object is placed between the focus and the center of
curvature?
Answer: When the object is placed between the focus and the center of curvature of a concave mirror, the image formed is virtual, upright, and magnified. The image is larger in size than the object. It is formed on the same side as the object, and it is virtual because the reflected rays do not actually converge at a point.
8.
Describe the construction and working of a shaving mirror (concave
mirror) and a rear-view mirror (convex mirror).
Answer: Shaving mirror (concave mirror): When a person looks into the mirror, the concave surface reflects light rays in a way that forms an upright and magnified image of the face. This allows for a closer and clearer view while shaving.
Rear-view mirror (convex mirror):
A rear-view mirror in a vehicle is usually a convex mirror.
When a driver looks into
the rear-view mirror, the convex surface reflects light rays in a way
that forms a smaller, wider, and slightly distorted image. This helps
the driver to have a better view of the surroundings and other
vehicles.
9.
Define magnification. Write its units and formula.
Answer: Magnification is the ratio of the size of the image to the size
of the object. It is a measure of how much larger or smaller the image
is compared to the object. Magnification is dimensionless and
has no units. Formula:
Magnification = Height of Image / Height of Object.
10. Define Reflection of Light.
Reflection:
When ray of light is incidence on a surface making some angle with the
normal and reflected back in the same medium by making same angle with
the normal is called reflection.
11. What are laws of Reflection of Light?
Law of reflection:
(i) angle of incidence = angle of reflection
(ii) Normal ray, incident ray & reflected ray at point of incidence all lie in same plane.
12. Write Properties of image formed by plane mirror.
(i)
Virtual & Erect
(ii)
Laterally inverted
(iii)
Same size and at same distance from object
13. Give Uses of concave mirror, convex mirror and concave lens and convex lens.
Uses of Concave mirror:
Shaving mirror, make-up mirror, dentist mirror, torches and headlights,
reflector for projector lamps, solar devices and furnace.
Uses of Convex mirror: rear-view mirrors in vehicles, reflector in streetlights.
Uses of Concave lens:
In spectacles for correcting myopia.
Uses of Convex lens:
in simple and compound microscope, telescope, camera spectrometer,
spectacles for correcting hypermetropia.
14. Define magnification Give formula and units and how it is helpful to find out the properties of image.
Magnification: Ratio of height of image to the height of object.
Formula: m = height of image / Height of object
Units: It has no units.
m = +ve means image is virtual and erect.
m = -ve means image is real and inverted.
m= 1 : image is same size as object
m<1 : image is smaller than the object.
m>1 : image is larger than the object.
15. Give difference between Real and Virtual image.
|
Real Image |
Virtual Image |
|
It is always inverted. |
It is always erect. |
|
It forms on the screen. |
It not forms on screen. |
|
Rays actually meet. |
Rays appear to meet. |
|
Magnification value is negative. |
Magnification value is positive. |
16. Give mirror Formula.
Mirror Formula:
17.
For which mirror and lens value of focal length will be Positive and
Negative.
Positive focal length is of convex lens and mirror and negative focal length is of concave lens and mirror.
18.
What do you mean by the magnification (m) If value of m=2 m=-1
It is defined as the ratio of height of image to the height of object. If m= 2 it means image is virtual erect and large in size. If m= -1, It means image is real and inverted and same in size.





0 Comments
Please don't give write any spam link.