Class 10- NCERT Notes Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations-CBSE HUB ONLINE

CBSE class 10 science chemical reactions and equations notes
pdf will provide a brief overview for your quick Revision. Here class 10
Science chemical reactions and equations class 10 notes pdf download. If You
want to know about all the class 10 science chemical reactions and equations.
You Just have to read this full post. Here, our Well Qualified team have shared
there full experience to class 10 science chemical reactions and equations explanation.it
is Completely ncert class 10 science chemical reactions and equations notes. If
Want to give the class 10 science chemical reactions and equations mcq online
test. Please Click on the Following Link.
Chemical reactions and equations Online Test
For this Online test we have choosen best and
Important MCQs for Your cbse class 10 science chemical reactions and equations mcq.
Which Will be Very helpful for your Competitive Exams because these are Fully
based on CBSE class 10 science chemical reactions and equations ncert Based.
Chemical Reaction: It is a chemical change in which one or more
substances react to form one or more products of entirely different properties
by undergoing a change in state, colour, temperature or due to evolution of
gas. Rearrangement of atoms also takes place in a chemical reaction
Chemical Equation: It is a representation of a chemical reaction in terms of standard symbols and formulae used for the reactants and the products. It comprises of reactants, products and an arrow - sign. For example, magnesium ribbon burns with oxygen present in the air to form a white powder of magnesium oxide, which can be represented as:
Balanced and Unbalanced Chemical
Equations:
Equation having an equal number
of atoms or masses of various elements in the reactants as well as products is
balanced chemical equation but that having an unequal number of both is an
unbalanced chemical equation.
Types of Chemical Reactions:
Chemical reactions are of the
following types:
1.
Combination
Reaction:
It is the reaction in which two or more
reactants combine to form a single compound. For example,
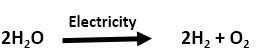
2. Decomposition Reaction:
It is the reaction in which a single reactant breaks up to give two or more simpler products. These reactions are carried out by applying heat (thermal decomposition), light (photochemical decomposition) or electricity (electrolysis or electrolytic decomposition). For example,
This reaction is known as electrolysis of water.
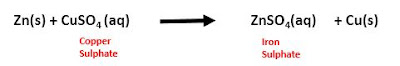
3. Displacement Reaction:
It is the reaction in which one element
takes the place of another element in a compound. A more reactive element
displaces a less reactive element from its compound. For example,
These reactions are also called single displacement reactions.
4. Double Displacement Reaction:
it is the reaction in which anions and
cations of two different reactant molecules interchange their positions to form
two extremely different compounds. For example,
These reactions are also called
precipitation reactions.
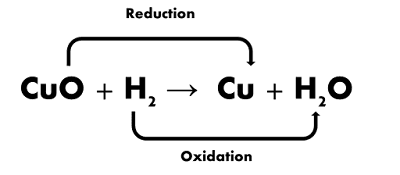
5. Oxidation and Reduction
Reactions or Redox Reaction:
(i)
Oxidation: In it, a substance gains oxygen or loses
hydrogen during a reaction
(ii)
Reduction: In it, a substance loses oxygen or gains
hydrogen during a reaction.
MNEMONICS
Concept: Definition of oxidation
and reduction
Mnemonics: OIL RIG Interpretation:
OIL = Oxidation Is Loss ( of hydrogen)
RIG = Reduction Is Gain (of
hydrogen)
(iii) Redox Reaction: In it, oxidation and reduction occur simultaneously.
Redox is the short form of reduction oxidation-Reduction.
Exothermic Reactions:
These are the reactions in which
heat is released along with the formation of products. For example,
respiration.
Endothermic Reactions:
These are the reactions in which heat is absorbed along with the formation of products. For example, melting of ice to form water. Decomposition of Calcium Carbonate On Heating.
Corrosion:
It is the process of slow conversion of
metals into their undesirable compounds by the action of moisture, water, acids
and air. It causes damage to car bodies, bridges, iron railings, ships and
other metal objects of daily use.
The formation of rust
(reddish-brown coating of hydrated iron (III) oxide, Fe2O3.XH2O) on iron, green
coating on copper and black coating on silver are all examples of corrosion.
Corrosion can be prevented by applying a layer of oil and grease, or
coating the iron article with a thick layer of zinc (Galvanization);
Rancidity: It is the phenomenon in which food items containing and fats when exposed to air give an unpleasant smell and this is due to oils and fats present in the food items getting oxidize by air, heat and light. The methods to prevent rancidity are:
- Keeping food in air-tight containers.
- By adding antioxidants to food.
- By packaging fat and oil containing food with nitrogen.

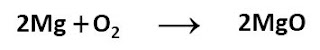

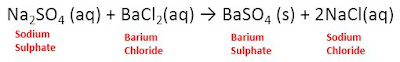




0 Comments
Please don't give write any spam link.