Acids, Bases and Salts Class 10 Chapter 2 Notes
CBSE class 10 science acids and bases notes pdf will provide a brief overview for your quick Revision. Here class 10 Science acids, bases and salts class 10 notes pdf download. If You want to know about all the class 10 science acids bases and salts. You Just have to read this full post. Here, our Well Qualified team have shared there full experience to class 10 science acids,bases and salts explanation.it is Completely ncert class 10 science acids, bases and salts notes. If Want to give the class 10 science acids,bases and salts mcq online test.
Please Click on the Following Link. Acids,Bases and Salts Online test
For this Online test we have choosen best and
Important MCQs for Your cbse class 10 science acids,bases and salts mcq. Which
Will be Very helpful for your Competitive Exams because these are Fully based
on CBSE class 10 science acids,bases and salts ncert Based.
Indicators:
These are the chemical substances which give different Colours in acidic and basic solutions. Litmus solution and turmeric are natural indicators. Methyl orange and phenolphthalein are Synthetic indicators. Vanilla, onion and clove are used to determine the presence of acids and bases with their smell, hence they are called olfactory indicators.
Universal Indicator:
It is a mixture of many different indicators
(or dyes) which give different colours at different pH values to indicate the
acidity and alkalinity of solutions.
Acids:
The substances which are sour in taste and turn
blue litmus solution to red colour are called acids. Some fruits like lemon,
orange, tamarind, etc. are sour in taste due to presence of acid in them.
According to Arrhenius, acids are hydrogenous substances and releases hydrogen ions (H+) in aqueous solution, e.g., HCI (Hydrochloric acid), H2SO4 (Sulphuric acid), HNO3 (Nitric acid), CH3COOH (Acetic acid), H2CO3 (Carbonic acid), H2SO3 (Sulphurous acid), etc.
Chemical Properties of Acids:
1. Reaction with Metals:
When acids react with metals, they produce a salt and hydrogen gas. Most metals react with acids, but not all.
For example, .
For example,
3. Neutralisation Reaction:
It
is the reaction between an acid and a base to give salt and water.
For example,
4. Reaction with Metal Oxides:
An acid reacts with a metal oxide/hydroxide to form salt and water. For example,
According to Arrhenius, they give hydroxide ( OH - ) ions are bases but all bases may not be alkalies.
Chemical Properties of Bases
1. Reaction with Metals: Only top reactive metals such as sodium and ( potassium) react with bases to form salt and hydrogen gas. For example,
It is a scale used to measure the
concentration of H+ ions in a solution. One can measure pH from zero
(very acidic) to fourteen (very alkaline) on this scale. Higher the value of
hydrogen ion, lower will be its pH value. Also, as pH increases, the
concentration of OH ions also increases and therefore the strength of the base
also increases. 7 indicates neutral pH.
Importance of pH in Everyday
Life:
(i)
Our body works in the pH range of
7.0 to 7.8.
(ii) Change in pH (less than 5.6) of rain causes acid rain, which has harmful effects on aquatic life.
(iii)
Plants require a specific pH
range for their healthy growth.
(iv)
Tooth decay starts when pH of
mouth is lower than 5.5.
pH of Salts:
(i) Salt of a strong acid and a strong base is neutral in nature with pH value of 7.
(ii) Salt of a strong acid and a weak base is acidic in nature with pH value less than7.
(iii) Salt of a strong base and a weak acid is basic in nature with pH value more than7.
Common Salt: Sodium chloride obtained from sea is also known as common salt. The large crystals of common salt found in underground deposits are called rock salt.
Some Compounds Obtained from Common Salt:
1. Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH): When electricity is passed through an aqueous solution of sodium chloride (brine), the salt undergoes decomposition to produce sodium hydroxide solution near the cathode, chlorine gas at the anode and hydrogen gas at the cathode.This process is called chloro-alkali process because of the products formed-chloro for chlorine and alkali for NaOH.
2. Bleaching Powder (CaOCl2): When chlorine gas is passed through dry slaked-lime [Ca(OH)2], bleaching powder (CaoCl2) is obtained.
3. Baking Soda (NaHCO3): It is used for making baking powder and as an ingredient of antacids. It is also used in soda-acid fire extinguishers.
The following reaction takes place when baking soda is heated during cooking.
4. Washing Soda (Na2CO3.10H20): Washing soda is obtained by recrystallisation of sodium carbonate. It is a basic salt.
5. Plaster of Paris (CaSO4 .1/2 H2O)
It is prepared by heating gypsum (CaSO4.2H2O) at 373K causing it to lose water molecules and becoming calcium sulphate hemihydrate.
It is used for making toys,
materials for decoration and for making smooth surfaces.
Water of Crystallisation:
It is the fixed number of water
molecules present in one formula unit of a salt. The salts which contain water
of crystallisation are called hydrated salts. For example, Gypsum crystals
contain two molecules of water of crystallisation. It has the chemical formula,
CaSO4.2H2O.
When
hydrated salts are heated strongly, they lose their water of have lose
crystallisation. The salts which crystallisation are called anhydrous salts.
For latest Updates Subscribe to Our Youtube Channel - Study Vitamin






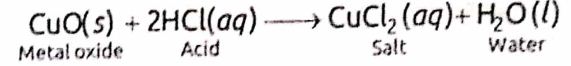









0 Comments
Please don't give write any spam link.